Summary Card
=================================== RECOMMENDATION: hold | STRENGTH: 65.0/100 | CONFIDENCE: 65.0%
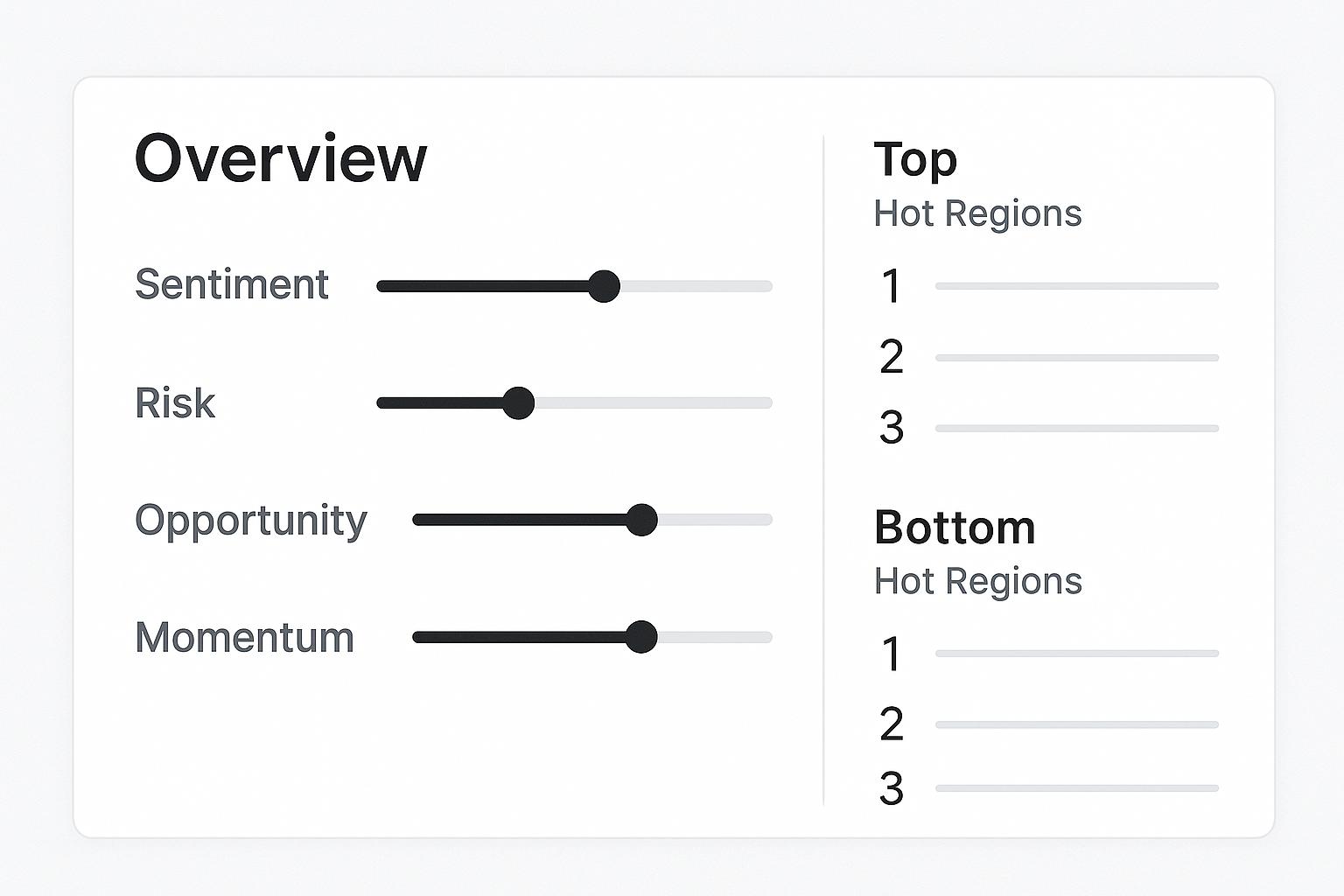
SENTIMENT Sentiment: [=========>] -166.5% RISK Risk: [=====>----] 56.2% OPPORTUNITY Opportunity: [===>------] 35.0% MOMENTUM Momentum: [>---------] 0.0%
TOP GAINERS: Major tanker and LNG shipping companies, AI for chartering and optimisation TOP LOSERS: Global container carriers (Maersk, COSCO, MSC, CMA CGM, Hapag-Lloyd), Sanctions-linked shadow fleet operators, Houthi movement HOT REGIONS: China / East Asia, Red Sea / Suez Canal
Market sentiment is negative, opportunity is weak, and momentum is falling across the period.
Trading Signal
hold - Strength: 65.0/100 | Confidence: 65.0%
Despite a deeply negative sentiment reading and strongly falling momentum, the composite model does not meet the thresholds for a "sell" or "avoid" signal because aggregate risk (56.2/100) and opportunity (35/100) are elevated but not extreme, and confidence is moderate at 0.65. Instead, the signal stack supports a "hold" recommendation, reflecting a view that structural headwinds from "Container freight rate decline / oversupply" and rising risks around "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement" and "Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting" are partly offset by targeted upside in tanker- and LNG-related themes. The high volatility score (0.89) further reinforces the case for maintaining, rather than aggressively increasing or cutting, exposure until either the oversupply or the sanctions/security narratives break more decisively.
Key Drivers: Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement, Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting, US–China port fees and maritime trade policy
Executive Summary
Key Takeaways
Full Explainer
Across the merged dataset, the forward-looking signal stack is dominated by structurally negative sentiment (headline sentiment score around -4.3) and a clear downward momentum reading (-1.0), with risk moderately elevated (56.2/100) and volatility high (0.89). Opportunity is present but constrained (35/100), indicating that upside pockets exist but are outweighed by pervasive downside pressure. Confidence in these signals is moderate at 0.65 with full evidence coverage (400 items), suggesting that the directional picture is reasonably robust even though sentiment itself is volatile.
Rising themes are concentrated around policy, security and energy-shipping dynamics. "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement", "Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting" and "US–China port fees and maritime trade policy" are the most prominent, followed by opportunity-tilted themes in "LNG exports, shipping and bunkering", "Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness", "Port congestion, rerouting and supply-chain reconfiguration" and "Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero". At the entity level, China and the Houthi movement are the key rising actors, alongside sanctions-linked shadow fleet operators and major tanker and LNG shipping companies, while the United States, Russia, the European Union and the large global container carriers remain structurally important but comparatively stable. Container freight rate decline and oversupply remains a high-weight, stable backdrop rather than a newly accelerating driver.
Given the client's focus on forward-looking signals, the composite trading logic interprets this pattern as a configuration where negative momentum and rising risk clusters are offset by specific, more targeted opportunities rather than by broad-based improvement. With sentiment deeply negative but aggregate risk and opportunity readings not extreme, and with moderate confidence in the signals, the model resolves to a baseline "hold" recommendation rather than a directional "buy" or "sell", pending clearer evidence that either the oversupply/rate-collapse or the sanctions/chokepoint narratives are decisively breaking one way or the other.
Recent external data show U.S. LNG exports reaching a record 10.1 million tonnes in October 2025, reinforcing the internal identification of "LNG exports, shipping and bunkering" as a key forward opportunity cluster.(reuters.com) At the same time, a 14.2% year-on-year rise in Suez Canal revenues between July and October 2025 points to a partial easing of Red Sea chokepoint stress relative to the internally rising "Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting" theme.(reuters.com)
Market Context
Key Takeaways
Full Explainer
The market tone captured in the dataset is distinctly risk-biased. The merged sentiment indicator is strongly negative (around -4.3), while the aggregate momentum score of -1.0 and an overall "falling" direction confirm that deterioration rather than recovery is the prevailing dynamic. Risk is moderately high at 56.2/100 and volatility is elevated at 0.89, implying that conditions are unsettled but not yet at extreme-stress levels. No specific entities or themes of interest were provided by the client, so this tone reflects the broad composite rather than a narrower, pre-filtered subset.
Momentum behaviour over time shows one particularly sharp deterioration, with a large negative period-over-period move of -20.75, preceded and followed by smaller but still negative shifts (-0.4, -0.15 and -0.18). The small positive acceleration rate (0.07) and two identified momentum inflection points between periods 2–3 and 3–4 suggest that the pace of deterioration has changed, but without yet delivering a decisive improvement; instead, the trend appears to be one of persistent, grinding weakness.
Regulatory and policy forces are a central part of the context. "US port fee policies" and "Sanctions and export-control enforcement" carry the heaviest regulatory weights, with "China port fee policies" and "IMO Net-Zero and carbon measures" also significant, and "CBAM and EU carbon policies" emerging as a smaller but non-negligible factor. Taken together, these point to a regime in which port charges, trade policy and decarbonisation measures are active drivers of forward risk and opportunity rather than background noise.
Structural and supply-chain dynamics reinforce this picture. The supply-chain map highlights "Port congestion and throughput / gateway shifts" and "Rerouting via Cape of Good Hope / longer voyages" as the largest operational drivers, with "Inventory adjustment and frontloading", "Blank sailings and capacity withdrawal", "Nearshoring and sourcing shifts" and "Floating storage and oil-on-water" providing additional levers of capacity and route flexibility. At the macro level, a "Global goods demand slowdown" and "Energy market reconfiguration and fuel costs" frame the demand and cost backdrop, while the defence map's "Naval deployments and maritime security operations" underscores that security operations are now structurally embedded in the maritime environment.
Geographically, exposures are concentrated in "China / East Asia" and the "Red Sea / Suez Canal" corridor, with "United States / North America" also material and secondary contributions from "Europe ports", the "Indian Ocean / Somalia region", the "Gulf of Aden", the "Panama Canal", "India" and the "Strait of Hormuz". This regional pattern aligns with the dominant themes in the signal stack: East–West trade lanes, Middle Eastern chokepoints and US–China policy frictions are at the core of the forward-looking risk and opportunity landscape.
External evidence indicates that energy-linked shipping demand is being supported by exceptionally high U.S. LNG export volumes to Europe, consistent with the model’s LNG and tanker-strength signals.(reuters.com) In parallel, improved security conditions in the Red Sea have allowed Suez Canal traffic and revenues to recover versus the period of intensive Houthi attacks, softening, but not removing, the chokepoint risk backdrop captured in the dataset.(reuters.com)
Trend Analysis
Key Takeaways
Full Explainer
Trend-wise, the dataset points to a broad-based deterioration anchored in a persistent oversupply backdrop. "Container freight rate decline / oversupply" carries the single largest thematic weight and is classified as stable rather than rising or falling, indicating that rate pressure is a standing structural condition rather than a newly emerging shock. Against this backdrop, the overall momentum profile is still judged "falling", with the composite momentum score at -1.0 and all period-over-period changes negative, which means that other themes are worsening on top of an already weak base.
The clearest rising themes cluster around sanctions, security and policy. "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement" and "Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting" show strong weights alongside "US–China port fees and maritime trade policy", signalling that compliance pressure, grey-fleet dynamics and route insecurity are all becoming more prominent forward drivers. Additional rising themes include "LNG exports, shipping and bunkering" and "Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness", which together describe a tightening tanker and LNG segment, as well as "Port congestion, rerouting and supply-chain reconfiguration" and "Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero", which add operational and regulatory complexity to the outlook.
There are no major falling themes identified in the current trend diagnostics, and the only large, non-rising theme is the stable but heavy-weight "Container freight rate decline / oversupply". This absence of clearly improving themes reinforces the interpretation that the negative momentum is being driven by the intensification of sanctions, security and policy narratives rather than by any meaningful easing of structural headwinds.
Across time, the two identified inflection points between periods 2–3 and 3–4 indicate changes in the slope of momentum rather than a reversal of direction. The very sharp deterioration in one period (-20.75) followed by smaller but still negative changes (-0.15 and -0.18) suggests that the most acute phase of weakening may have passed, but the signal has not yet turned; instead, sanctions, chokepoint security and trade-policy themes appear to be sustaining a lower plateau of confidence and sentiment. For a client focused on forward signals, this pattern emphasises monitoring the evolution of these rising themes for any sign that they are peaking or broadening further.
Rising Themes
| Theme | Current Weight | Prior Weight | Delta | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement | 21.8 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting | 19.8 | , | , | Accelerating |
| US–China port fees and maritime trade policy | 18.7 | , | , | Accelerating |
| LNG exports, shipping and bunkering | 13.2 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness | 12.1 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Port congestion, rerouting and supply-chain reconfiguration | 8.5 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero | 8.5 | , | , | Accelerating |
Falling Themes
| Theme | Score | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| None identified | - | No falling themes flagged in current dataset |
Exposure Assessment
Key Takeaways
Full Explainer
Risk exposure in this dataset is concentrated in a small number of clearly defined clusters. "Market oversupply and rate collapse" is the largest single risk theme, closely followed by "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement risks" and "Chokepoint and route security (Red Sea, piracy)". "Port fee and trade-policy fragmentation" is the next tier, with "Operational and port-disruption risks" and "Regulatory fragmentation and IMO uncertainty" rounding out the risk map. Together, these indicate that earnings and asset-value risk is being driven primarily by freight-rate compression, sanctions and compliance exposure, and route security rather than by idiosyncratic or company-specific issues.
On the upside, opportunity is concentrated in a more targeted set of themes. "LNG exports, shipping and bunkering" and "Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness" highlight potential upside in energy-linked shipping capacity and rates, while "Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero" points to structural investment and differentiation opportunities linked to regulatory alignment. The AI map, with "AI for chartering and optimisation", "Real-time tracking and compliance" and "Predictive logistics and visibility", suggests incremental upside from efficiency and compliance technologies that can mitigate some of the operational and regulatory risks elsewhere in the stack.
Vulnerabilities arise where negative or stable momentum intersects with high risk. The combination of a heavy, stable "Container freight rate decline / oversupply" backdrop with explicit "Market oversupply and rate collapse" risk implies that segments most exposed to spot container rates carry structurally asymmetric downside. At the same time, rising "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement" and "Chokepoint and route security" themes indicate that exposure to opaque fleets, insecure routes or weak compliance capabilities could amplify loss risk if enforcement or security conditions tighten further.
Operational sensitivities are dominated by "Port congestion and throughput / gateway shifts" and "Rerouting via Cape of Good Hope / longer voyages", which together describe capacity and routing constraints that can lengthen voyages and reallocate volumes between gateways. "Inventory adjustment and frontloading" and "Blank sailings and capacity withdrawal" expose supply chains to timing and utilisation risk, while "Nearshoring and sourcing shifts" and "Floating storage and oil-on-water" highlight the potential for structural rewiring of trade patterns. These operational levers interact directly with the risk map, shaping how oversupply, sanctions and chokepoint themes ultimately translate into realised exposure.
Strategic Implications
Key Takeaways
Full Explainer
From a strategic allocation perspective, the signal configuration favours selective overweighting of segments aligned with rising opportunity themes while maintaining caution around structurally challenged areas. Within shipping, this points to relatively stronger positioning towards the "LNG exports, shipping and bunkering" and "Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness" clusters, where rising thematic weight coincides with the opportunity narrative, and towards assets and strategies that are leveraged to "Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero" and the AI-enabled efficiency themes in chartering, tracking and predictive logistics.
Conversely, the combination of a heavy, stable "Container freight rate decline / oversupply" theme with explicit "Market oversupply and rate collapse" risk argues for underweight or highly selective exposure to capacity segments that are most sensitive to container spot rates and volume swings. Rising "Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement" and "Port fee and trade-policy fragmentation" also suggest caution around structures that rely on opaque fleets, marginal compliance or concentrated exposure to contested tariff and fee regimes.
Time-horizon sensitivity is captured in the momentum profile: the overall direction is falling, with a sharp single-period deterioration followed by smaller but still negative moves and a modest positive acceleration rate. In practical terms, this implies that downside pressure may persist in the near term, but with the worst of the step-change likely already realised; strategic decisions therefore need to distinguish between positioning for continued weak conditions versus positioning for eventual normalisation once sanctions, security and policy themes stabilise.
Policy and regulatory considerations remain central to any strategy built on this signal set. "US port fee policies", "China port fee policies" and "Port fee and trade-policy fragmentation" point to a fragmented and shifting tariff environment, while "Sanctions and export-control enforcement", "IMO Net-Zero and carbon measures" and, to a lesser extent, "CBAM and EU carbon policies" indicate that compliance and decarbonisation trajectories are key differentiators. Structurally, the supply-chain map’s emphasis on port congestion, rerouting via longer voyages and nearshoring suggests that bottlenecks and route reconfiguration should be treated as persistent features rather than transient anomalies when calibrating exposure.
Core Analytics
Signal Metrics
| Signal | Score | Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentiment | -4.33 | -1 to 1 | Negative |
| Risk | 56.2 | 0 to 100 | Moderate |
| Opportunity | 35.0 | 0 to 100 | Moderate |
| Momentum | -1.00 | -1 to 1 | Decelerating |
| Volatility | 0.89 | 0 to 1 | High |
Momentum Ladder
| Rank | Theme | Momentum | Direction | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Container freight rate decline / oversupply | 28.8 | → | n/a |
| 2 | Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement | 21.8 | ↑ | n/a |
| 3 | Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting | 19.8 | ↑ | n/a |
| 4 | US–China port fees and maritime trade policy | 18.7 | ↑ | n/a |
| 5 | LNG exports, shipping and bunkering | 13.2 | ↑ | n/a |
| 6 | Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness | 12.1 | ↑ | n/a |
| 7 | Port congestion and throughput shifts | 8.5 | ↑ | n/a |
| 8 | Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero | 8.5 | ↑ | n/a |
Entity Performance
Positive Sentiment
| Entity | Sentiment | Mentions | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major tanker and LNG shipping companies | Positive | – | Rising |
| AI for chartering and optimisation | Positive | – | Unclassified |
Negative Sentiment
| Entity | Sentiment | Mentions | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Houthi movement | Negative | 11.0 | Rising |
| Global container carriers (Maersk, COSCO, MSC, CMA CGM, Hapag-Lloyd) | Negative | – | Stable |
| Sanctions-linked shadow fleet operators | Negative | – | Rising |
Theme Movement
Rising Themes
| Theme | Current Weight | Prior Weight | Delta | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanctions, shadow fleet and enforcement | 21.8 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Red Sea / Suez security and rerouting | 19.8 | , | , | Accelerating |
| US–China port fees and maritime trade policy | 18.7 | , | , | Accelerating |
| LNG exports, shipping and bunkering | 13.2 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Tanker market strength / VLCC tightness | 12.1 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Port congestion, rerouting and supply-chain reconfiguration | 8.5 | , | , | Accelerating |
| Maritime decarbonisation and IMO Net-Zero | 8.5 | , | , | Accelerating |
Falling Themes
| Theme | Score | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| None identified | - | No falling themes flagged in current dataset |
Geographic Distribution
| Region | Activity | Sentiment | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| China / East Asia | High (8.2) | , | , |
| Red Sea / Suez Canal | High (7.5) | , | , |
| United States / North America | Medium (5.2) | , | , |
| Europe ports | Low (1.5) | , | , |
| Indian Ocean / Somalia region | Low (1.0) | , | , |
| Gulf of Aden | Low (0.9) | , | , |
| Panama Canal | Low (0.8) | , | , |
| India | Low (0.8) | , | , |
| Strait of Hormuz | Low (0.6) | , | , |
Trading Signal Breakdown
| Signal Component | Value | Weight | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentiment | Negative | 30.0% | Negative sentiment bias (toward Sell/Avoid) |
| Momentum | Weak (falling) | 25.0% | Falling momentum, reinforces cautious stance |
| Risk-adjusted | Unfavourable | 45.0% | Risks outweigh opportunities, but not at extreme-stress levels |
| TOTAL | Hold | 100.0% | Net: Hold (65.0 strength, 65.0% confidence) |
Client Question
This section is reserved for specific questions added to the original report request. In future, please include a company, product, or topic for targeted analysis.
External Context
The external validation that LNG export flows are running at record levels supports the internal tilt towards opportunity in LNG and tanker-linked exposures, even within an overall "hold" stance.(reuters.com) Evidence of improving Suez Canal utilisation and reduced diversions suggests that some of the most extreme Red Sea disruption risks are receding, which modestly tempers the downside pressure associated with the internal container and chokepoint narratives without reversing them.(reuters.com)
Report Generated: 2025-11-21 00:00:00 UTC Noah Wire Services - Institutional Intelligence