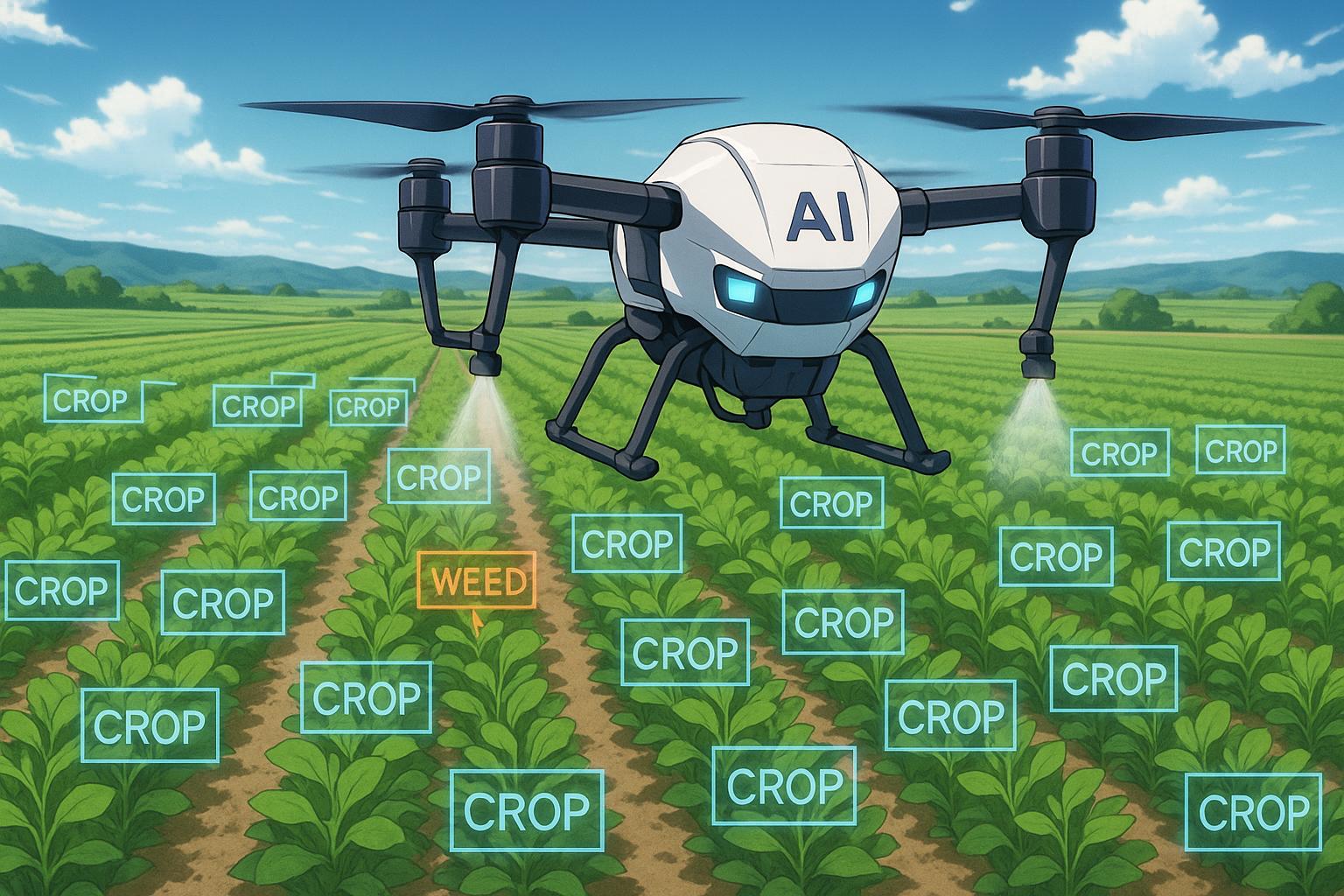
Precision AI is carving a niche in the agricultural technology sector with its innovative approach to drone-assisted farming. The company claims its autonomous aerial system is designed not only to aid farmers in making more informed decisions but also to significantly reduce operational costs. Daniel McCann, the CEO of Precision AI, highlights the real-time capabilities of their technology, which combines artificial intelligence with advanced imaging systems. This setup allows the drone to scan fields autonomously, successfully distinguishing between crops and weeds. McCann asserts, “The AI actually runs in real-time… It can actually differentiate between weeds and crop and precision spray just when there’s weeds present.”
This capability presents notable advantages over traditional ground-based sprayers, including a significant reduction in soil compaction and increased timing flexibility in agricultural applications. In a comparative trial between their aerial technology and conventional ground spraying methods, Precision AI reported an impressive 83% reduction in pesticide use without compromising weed control efficacy. McCann indicates that the company is currently conducting additional field trials, anticipating a limited commercial rollout of their technology by 2026, with broader availability expected the following year.
The concept of using drones in precision agriculture is not novel; however, the continual advancement of these technologies underscores a growing trend within the industry. For instance, other companies like Rotor Technologies and Guardian Agriculture are also making strides in this field. Rotor Technologies is working on unmanned helicopters capable of crop spraying and emergency applications, showcasing prototypes that prioritise safety and efficiency in agricultural practices. Their innovations are part of a broader push to enhance the traditional methods of aerial application, especially in light of the high accident rates associated with human-piloted crop dusters.
Guardian Agriculture's SC1 is another noteworthy development in this space. Recently approved by the FAA, the SC1 is an electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft designed for efficient crop dusting operations. With a payload capacity of 200 pounds and the ability to cover up to 60 acres per hour, it offers a promising alternative to both traditional aircraft and smaller drones. Together, these technologies reflect a shift towards more automated and precise agricultural practices, utilising advanced data analytics and AI-driven insights.
The advantages of employing drones in precision agriculture extend beyond simply applying pesticides and fertilisers more effectively. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors enable the detailed monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and nutrient levels, which is crucial for optimising resource usage and enhancing productivity. The data captured allows for timely interventions—such as addressing pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies—thereby minimizing chemical usage and fostering sustainable farming.
The transformative potential of drones, powered by AI, is significant. Research suggests that AI-enhanced farming could yield a stunning increase in global productivity, potentially raising crop yields by up to 70% by 2050 and diminishing pesticide applications by as much as 90%. With these tools at their disposal, farmers are increasingly equipped to manage their resources more judiciously while contributing to a more sustainable agricultural future.
However, the integration of these high-tech solutions isn't without challenges. The initial investment required for adopting AI and drone technology can be a substantial barrier, particularly for smaller farms. Moreover, accessibility to such advanced tools can be limited in rural areas, hindering widespread adoption. Despite these hurdles, the overall trajectory points toward a future where autonomous equipment and AI not only revolutionize agricultural practices but also play a critical role in addressing global food security issues.
📌 Reference Map:
Source: Noah Wire Services