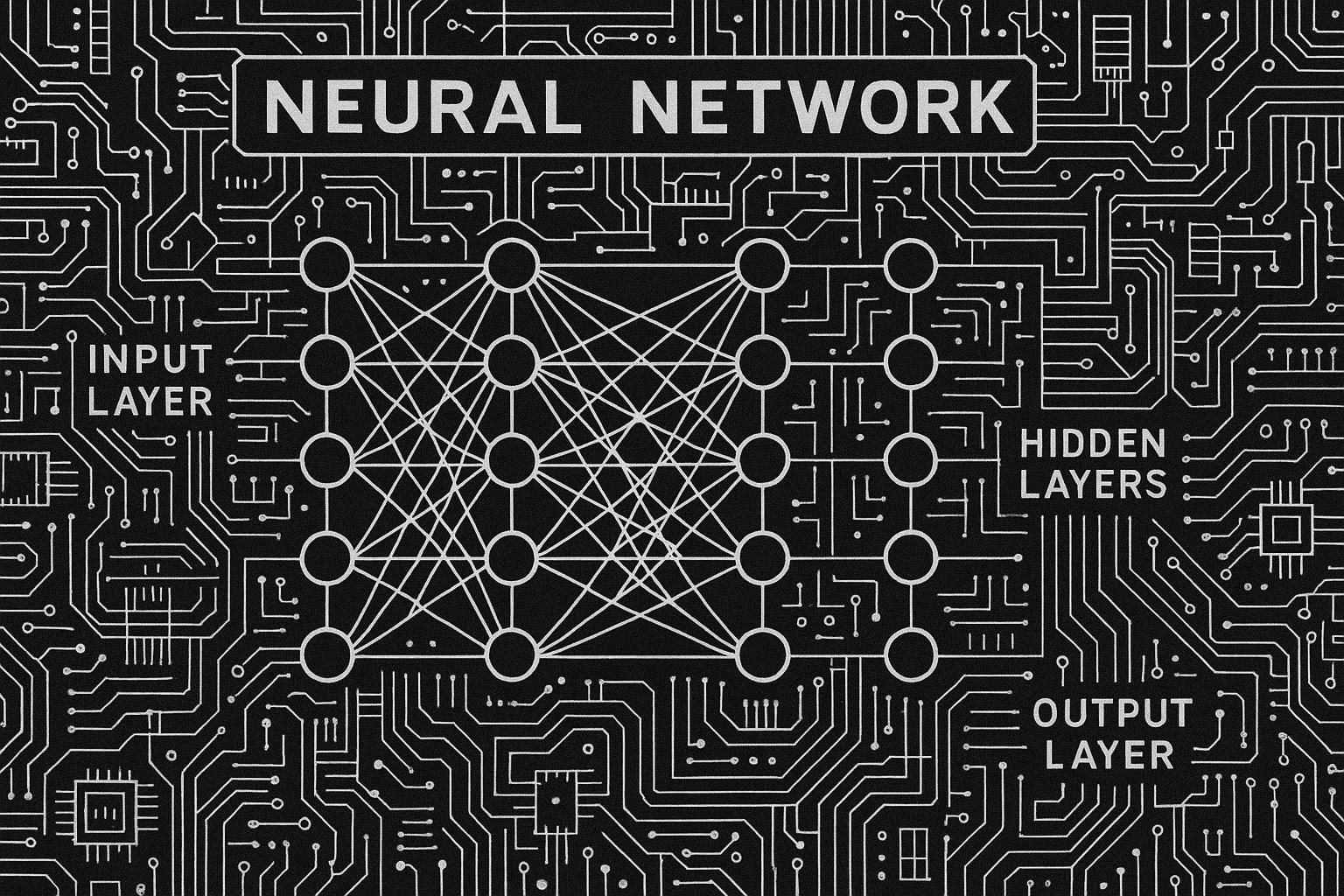
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become central to the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, offering capabilities that span generating human-like text, answering complex questions, translating languages, and summarizing information. Recent efforts to visualise and demystify the inner workings of LLMs have gained traction, aiming to make this sophisticated technology more accessible to non-experts and foster broader AI literacy. Visual aids, such as a widely circulated infographic by the God of Prompt account on social media, succinctly break down key components of LLMs including tokenization (where text is segmented into smaller units), embedding layers that transform tokens into numerical representations, and transformer architectures that process sequences via attention mechanisms. These educational tools align with a broader industry push to clarify AI's mechanisms as the global AI market is projected to reach $184 billion by 2025, largely driven by advances in LLM technology.
The impact of LLMs extends deeply into multiple sectors. According to McKinsey & Company reports, these models have revolutionised natural language processing applications in customer service, content creation, and data analysis. For instance, e-commerce giants such as Amazon have harnessed LLMs for personalised product recommendations, reportedly boosting sales by up to 35%. Meanwhile, Microsoft’s integration of LLMs into its Azure cloud services has secured a significant 25% market share in the cloud AI domain. Financially, generative AI powered by LLMs could add between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy by 2030. However, the proliferation of LLMs demands careful navigation of challenges including data privacy, regulatory compliance, and substantial computational requirements. A Deloitte survey revealed that 40% of companies face hurdles scaling LLMs compliantly under frameworks such as the EU AI Act, effective from 2024. Strategies like federated learning, which train models without centralising sensitive data, offer promising solutions.
Technically, LLMs operate on transformer architectures first introduced in the seminal 2017 "Attention Is All You Need" paper. This design enables efficient parallel processing of sequences, a key to managing the enormous data these models require. Recent innovations such as Meta’s Llama series have reduced training time dramatically, allowing models to be fine-tuned locally on consumer hardware in days rather than months. Addressing issues like hallucinations—where models generate incorrect outputs—has led to the adoption of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which integrates external knowledge bases to improve accuracy. Efficiency gains continue with quantization techniques that shrink model sizes by up to 75% without substantial loss of performance, facilitating deployment on edge devices. Market data reflects these trends; for example, NVIDIA reported a 150% year-over-year surge in AI chip demand during Q2 2024, underscoring commercial momentum behind LLM training.
The competitive landscape of LLMs is both diverse and dynamic. OpenAI’s GPT series remains the market leader, with GPT-4o offering enhanced intelligence, reduced latency, and multimodal capabilities that process text, images, and audio in real time. GitHub Copilot, built on GPT-4, excels in code generation, while Meta’s Llama 3 provides an open-source, cost-effective alternative suitable for local use. Anthropic’s Claude 3 targets business users with its large context window and complex task reasoning, albeit at a higher cost. Other notable players include Alibaba’s Qwen-1.5 for multilingual chatbots and Google’s Gemini 1.5, specialised in translation with rich contextual understanding. Open-source initiatives such as EleutherAI's GPT-J foster innovation by democratizing access, while enterprises often blend Large and Small Language Models (SLMs) to optimise efficiency, accuracy, and data privacy — particularly in regulated sectors like law, finance, and healthcare where domain-specific precision is critical.
Ethical considerations remain paramount in LLM deployment. Guidelines from organisations like the Partnership on AI emphasise the necessity of regular bias audits and transparency, including the publication of detailed model cards describing capabilities and limitations. Regulatory frameworks, including the U.S. Executive Order on AI from 2023, underscore the importance of responsible deployment, prompting companies to invest in compliance and safety tools. Looking ahead, LLMs are expected to evolve further into multimodal systems by 2026, blending text, image, and audio processing, opening opportunities in media, entertainment, and real-time Internet of Things (IoT) applications. PwC’s Global Entertainment and Media Outlook forecasts a potential $500 billion market impact, while MarketsandMarkets predicts edge LLM deployments could grow to a $50 billion market by 2027. Practical business applications are already evident, from automating legal document reviews which reportedly reduce firm costs by 20-30%, to enhancing predictive analytics in supply chains.
For businesses seeking to implement LLMs, starting with cloud API services from providers like OpenAI is a common approach, with subsequent fine-tuning for specific applications balanced by robust data security measures. However, risks such as biased outputs and high energy consumption persist, requiring ongoing audits and adoption of efficient architectures. Meanwhile, educational initiatives that visualise and explain LLM inner workings are indispensable for fostering wider understanding and innovation, equipping developers, businesses, and stakeholders to navigate the expanding role of these powerful AI models.
📌 Reference Map:
- Paragraph 1 – [1][6] (Blockchain News)
- Paragraph 2 – [1][6] (Blockchain News), [2] (TechRadar)
- Paragraph 3 – [1][6] (Blockchain News), [3] (TechRadar)
- Paragraph 4 – [2] (TechRadar), [4] (TechRadar), [6] (Blockchain News)
- Paragraph 5 – [1][6] (Blockchain News), [5] (Time)
- Paragraph 6 – [1][6] (Blockchain News), [2] (TechRadar), [4] (TechRadar)
Source: Noah Wire Services